In the investing world, there is a long-standing debate about which instrument is better, option trading vs stock trading.
In reality, though there is no better in a final sense, there is only better for you.
Stock (Equities) Trading offers many upside potential and benefits that options do not. Options trading offers flexibility and strategy customization that is nearly impossible with regular stock trading.
This article will review the basics and potential advantages and disadvantages.
Finally, we will look at where each type of trading shines and where it may fall short.
Contents
-
-
-
-
-
- What Is Stock Trading?
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Stock Trading
- What Is Options Trading?
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Options Trading
- Other Factors To Consider
- Conclusion
-
-
-
-
What Is Stock Trading?
Stock trading is a common form of investing that involves buying and selling shares in publicly listed companies.
This allows investors to own a portion of the company and potentially earn profits through stock price appreciation or dividends.
It is a very popular way for individuals to participate in the financial success of these companies and potentially increase their wealth.
Stocks are often mentioned with buy-and-hold investing due to the ability to collect dividends and a small tax benefit that some stocks offer.
This is not always the case; some prefer to trade in and out of equities to maximize their profit with short-term price action.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stock Trading
Like any investment, stock trading has advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered before investing.
Advantages
Equity ownership is one of the key advantages of stock trading.
When you purchase a stock, you buy an actual company share.
This entitles you to a portion of the company’s financial benefits.
This is most commonly seen through share price appreciation, but dividends are also a way to participate in the company’s earnings.
Another advantage of trading stocks is the simplicity of analysis.
As you will see in the next section, options are significantly more complex.
Stocks reflect the company and the economic conditions as a whole.
If you are trading on a long-term horizon, picking stable companies means your investment is safer than start-ups.
This also means that if you are a short-term trader, the chart you look at is the actual prices you are trading.
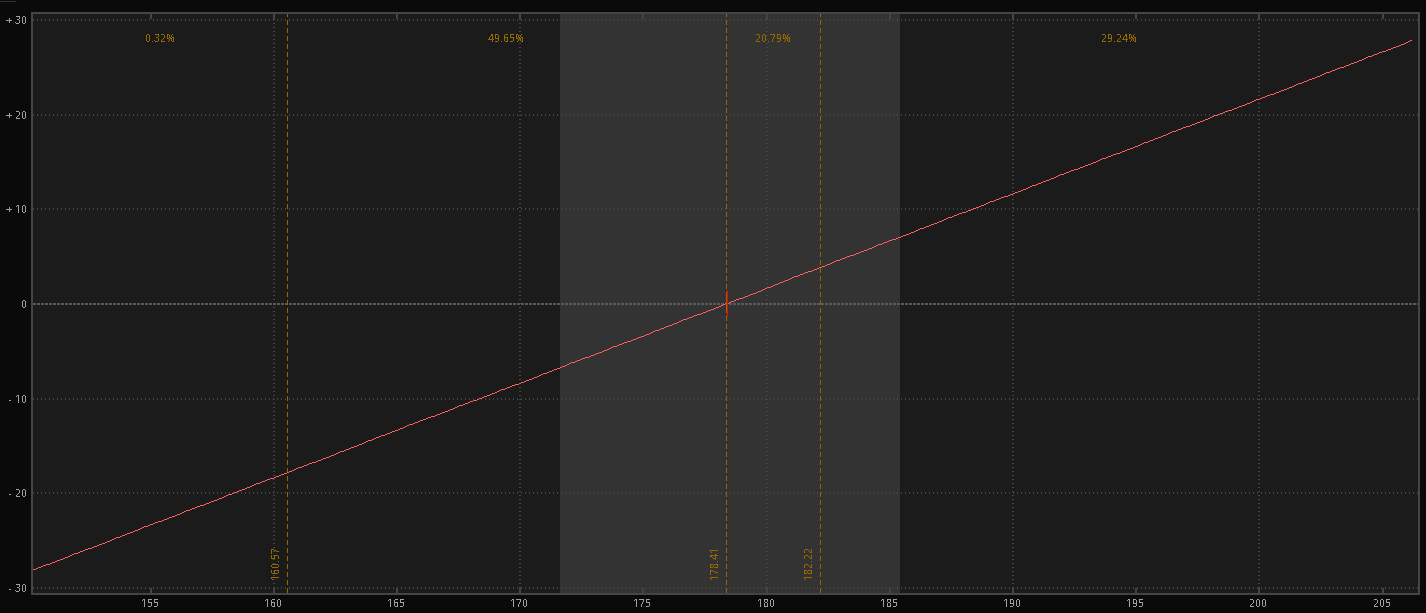
Take the risk profile of AAPL stock below.
As you can see, it’s completely linear, meaning that each dollar the stock appreciates or depreciates directly affects your PnL by that amount.
This makes it fairly simple to calculate the potential PnL of a move.
Disadvantages
Stocks also offer several disadvantages when compared to options.
First is the amount of capital required to trade.
Tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars are often required to buy into top-tier companies.
You can start with significantly less but need a larger account to see any real profits or income.
A second disadvantage is the inflexibility of stock trading.
The only two positions you have are long or cash unless you are a savvy trader.
You can short a stock to trade it down, but this requires margin, the ability to locate the shares, and a brokerage account that will allow you to trade it.
In addition to that, shorting the actual stock can be extremely risky as your potential loss is unlimited.
You will see in the options trading section that the opposite is true for most of these advantages and disadvantages.
What is Options Trading?
Where stock trading involves buying and selling the actual shares of a company, options trading involves contracts whose prices derive from the price movements of the underlying stocks.
Because of this, options are called derivatives, adding additional complexity to the trading.
Options are in two categories, calls and puts, and the basics are as follows: A call is a contract that lets you buy the underlying shares at a predetermined price and time (strike and expiration).
A put allows you to sell the underlying shares at a predetermined price and time.
Since options are contracts on the underlying stocks, you are not obligated to buy or sell the underlying shares as long as you buy the option.
All you need to do is close the option contract before the expiration, and your trade is closed.
Since options expire, they are often associated with short to intermediate holding times.
The longer you hold a contract that is not in the money, the less the contract is worth.
This makes them a favorite for short-term traders and as hedges against short-term market threats.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Options Trading
Much like stocks, options come with their distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Options are flexible, have a low entry cost, and often can produce some seriously outsized returns.
The downsides here, though, are the complexity of trading and analysis and the fact that they can expire worthless.
Advantages
One huge advantage of options is that starting capital is significantly lower than stocks. Smaller accounts with 5 to 10 thousand dollars can utilize the leverage to increase their returns and account size more rapidly than with stocks alone.
One reason for this is their leverage; each option contract allows the buyer to control 100 shares of the underlying stock.
Because of this, you will see an options price in the single dollar range when the underlying can be over $100 a share.
This same leverage is what allows long options to sometimes produce returns well over 100%
Another advantage of options trading is the flexibility it offers.
Unlike stocks, options allow the buyer to trade in both directions with a fixed loss amount.
If you buy a put for $200, your maximum loss is $200. In addition to the fixed-risk nature of straight calls and puts, buying and selling contracts to create a spread that actually pays you to trade is possible once you become more skilled in options trading.
These spreads can be used to trade all three market types: bullish, bearish, and range-bound.
This is the real allure of options to most traders.
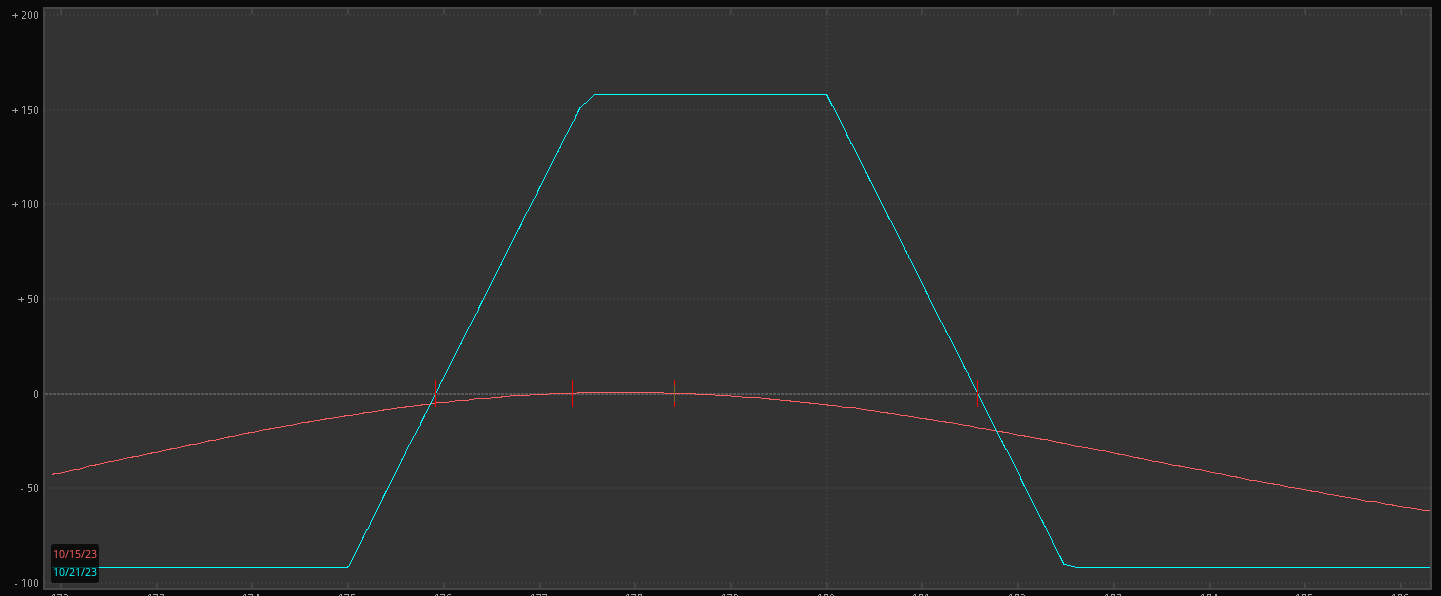
An example of such a spread is the iron condor, a neutral market strategy that captures profit from a range-bound stock.
An example risk profile of an Iron Condor is below. Notice how the maximum profit is capped on each side.
Disadvantages
Similarly to stocks, options also have a few significant disadvantages.
Ownership is the first disadvantage of an option. You don’t own anything because it’s a contract on the underlying stock.
If you buy a $200 call on AAPL and the stock closes at $198 on expiration day, your call option is worthless.
With a stock, you would still be in control of your shares.
Another disadvantage of options is that they are more complex to analyze.
In addition to analyzing the direction of the underlying stock, you also need to worry about the pricing factors for the options themselves.
A few of these include the time left on the contract (Theta), how close the strike is to the current price (Delta), and how volatile the underlying is (Implied Volatility).
These additional factors can make picking the correct contract or spread difficult for someone just starting.
Other factors to consider
Choosing between options and stocks requires an evaluation of a few personal goals and factors.
These include your investment goals, risk tolerance, trading style, and financial resources. In addition, you should consider the amount of time you can devote to trading.
Options often require more time to ensure your trade works out, whereas stocks can be a set-and-forget system.
Investment Goals
Your investment goals are the principal factor you should consider when choosing between stocks and options.
If you are looking for mostly appreciation with some dividends, such as in a retirement account, then stocks could be a better option.
If you are looking for the potential for growth or a more regular income stream, then options could be a better path to that goal.
Risk Tolerance
Secondary to your investment goals is your risk tolerance.
Good stocks are often considered a less risky investment, especially when compared to options contracts that have the potential to expire worthless or, worse, have a theoretical infinite loss.
Solid equities would often be a better choice than an options trade if you are fairly risk-averse.
If you are okay with some additional risk in exchange for some additional potential gain or cash flow, then options should be considered in your trading.
One important thing to remember is that risk tolerance is a gradient, not a choice.
So, as things change, your risk tolerance may adjust.
Also, adding options does not need to be an all-or-nothing endeavor.
Some more stable options trades, like covered calls, could be a great place to start with options.
Trading Style and Resources
Finally, you should consider your trading style and available resources.
Stock trading can be a more straightforward and passive approach but will often require significantly more capital to trade.
On the other hand, options trading will require active monitoring, understanding of the different strategies, and the ability to react quickly to market changes.
Options often also require significantly fewer resources than trading straight equities.
Conclusion
There you have it: a general overview of the differences between stock and options trading and what instrument could better fit you.
While both stocks and options offer distinct advantages, the final decision will almost always come down to your trading style and risk tolerance.
Stocks offer the trader a partial ownership and potential dividend incentive.
When you mix this with the ability to set and forget the trade, you get a long-term investor’s dream.
On the other hand, options offer a trade some significant flexibility and almost unlimited upside potential, but this comes at the cost of complexity.
Ultimately, it’s the trader’s choice, and while both are fantastic instruments, it’s important to know yourself and your trading style.
We hope you enjoyed this discussion on option trading vs stock trading.
If you have any questions, please send an email or leave a comment below.
Trade safe!
Disclaimer: The information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.

Original source: https://optionstradingiq.com/option-trading-vs-stock-trading/




